How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate data collection. Mastering drone operation isn’t just about pushing buttons; it’s about understanding the technology, adhering to safety protocols, and appreciating the legal framework governing their use. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly, whether you’re a novice pilot or seeking to refine your existing skills.
We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of this exciting technology.
From understanding basic controls and navigation to mastering advanced flight modes and camera techniques, we’ll explore every aspect of safe and effective drone operation. We’ll also delve into essential maintenance, legal compliance, and emergency procedures, equipping you with the knowledge to fly confidently and responsibly. This detailed guide will serve as your comprehensive resource for navigating the world of drone piloting.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures: How To Operate A Drone

Before you even think about taking your drone into the air, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring a safe and successful flight. This involves inspecting key components, verifying system functionality, and planning your flight path to avoid potential hazards. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, damage to your drone, or even injury to yourself or others.
Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection should cover several key areas. This includes verifying battery levels, inspecting propellers for damage, and ensuring a strong GPS signal. A systematic approach is essential for minimizing risks.
| Item | Check | Notes | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Sufficient charge (refer to manufacturer’s recommendations) | Low battery can cause unexpected power loss. | Charge battery if necessary. |
| Propellers | Inspect for cracks, damage, or looseness. | Damaged propellers can cause instability and crashes. | Replace damaged propellers. |
| GPS Signal | Strong signal with sufficient satellites acquired. | Weak GPS signal can lead to inaccurate positioning and flight instability. | Relocate to an area with better GPS reception if necessary. |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Check for smooth movement and proper functionality. | A malfunctioning gimbal can affect image quality. | Calibrate gimbal if necessary. |
| Drone Body | Inspect for any visible damage or loose parts. | Physical damage can compromise flight stability and safety. | Repair or replace damaged parts. |
Safe Drone Launch Procedure
Launching a drone safely requires careful planning and execution. Maintaining safe distances from obstacles and people is paramount. A step-by-step approach minimizes the risk of accidents.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning how to safely and effectively control your drone is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers. Ultimately, proficient drone operation requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of safety procedures.
- Choose a safe, open area away from obstacles and people (at least 50 feet).
- Power on the drone’s controller and wait for the GPS signal to lock.
- Power on the drone and wait for it to initialize.
- Slowly lift the drone vertically, keeping it within your line of sight.
- Monitor the drone’s altitude and position, making any necessary adjustments.
- Once the drone is airborne, move it slowly and carefully to avoid collisions.
Maintaining Safe Operational Distance
Maintaining a safe distance from bystanders and obstacles is crucial for preventing accidents. Always keep the drone within your visual line of sight, and be aware of your surroundings. Remember that unexpected events can occur, so being prepared for such situations is vital.
- Always maintain a safe distance from people and obstacles.
- Avoid flying over crowds or congested areas.
- Be mindful of the wind conditions and adjust your flight accordingly.
- Never fly near airports or other restricted airspace.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls and navigation system is fundamental to safe and effective operation. Different drones utilize various control methods, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Familiarity with these systems is crucial for confident piloting.
Drone Control Interfaces
Most drones use either joystick-based controllers or app-based interfaces on smartphones or tablets. Joystick controllers offer precise control, while app-based controls provide a more intuitive interface, often with features like automated flight modes. The choice depends on individual preferences and the drone’s capabilities.
Visual Representation of a Typical Drone Control Interface: Imagine a screen showing a miniature map of the drone’s location, with directional arrows for movement. Two joysticks would be displayed, one controlling altitude and yaw (rotation), the other controlling forward/backward and side-to-side movement. Buttons would be visible for functions like taking photos, recording video, and returning to home. A battery level indicator and GPS signal strength meter would also be prominent.
Drone Compass and GPS Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s compass and GPS ensures accurate flight and positioning. Inaccurate calibration can lead to erratic flight behavior and prevent features like Return-to-Home from functioning correctly. Proper calibration is a critical pre-flight step.
- Level the drone on a flat, stable surface.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for compass calibration (usually involving rotating the drone).
- Ensure a strong GPS signal before commencing flight.
Principles of Drone Navigation
Drone navigation involves understanding key concepts like altitude hold, waypoint navigation, and Return-to-Home functionality. These features enhance flight safety and efficiency, allowing for more complex maneuvers and autonomous operations.
- Altitude Hold: Maintains a consistent altitude, simplifying flight and reducing the risk of crashes.
- Waypoint Navigation: Allows the drone to follow a pre-programmed route, ideal for aerial photography and videography.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): Automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point, particularly useful in case of low battery or signal loss.
Flight Modes and Maneuvers
Modern drones often offer various flight modes, each designed for different skill levels and flight scenarios. Understanding these modes and their limitations is essential for safe and effective operation. Choosing the appropriate mode ensures the flight aligns with your skill level and the complexity of the maneuver.
Drone Flight Modes
Beginner mode limits speed and responsiveness, ideal for novice pilots. Sport mode allows for faster speeds and more aggressive maneuvers, requiring greater skill and experience. Other modes may include GPS mode, which relies heavily on satellite positioning for stability, and attitude mode, which relies more on the drone’s internal sensors.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness, enhancing stability and safety for beginners.
- Sport Mode: Allows for higher speeds and more aggressive maneuvers, suitable for experienced pilots.
- GPS Mode: Relies heavily on GPS for positioning and stability.
- Attitude Mode: Relies more on the drone’s internal sensors for orientation and stability.
Basic Drone Maneuvers
Mastering basic maneuvers like ascending, descending, hovering, and turning is fundamental to safe drone operation. These maneuvers form the building blocks for more complex flight patterns and aerial photography techniques.
- Ascending: Gently push the throttle stick upward.
- Descending: Gently pull the throttle stick downward.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady throttle position to hold the drone in place.
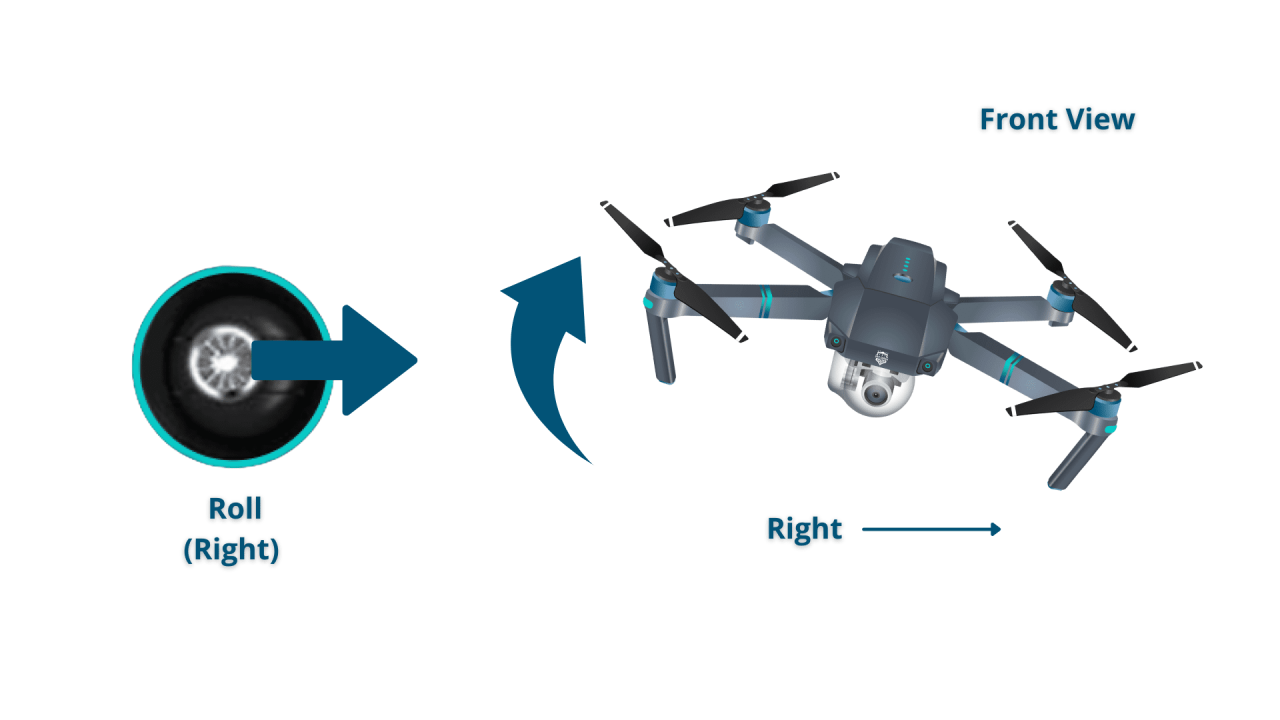
- Turning: Use the yaw control to rotate the drone left or right.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers, such as flips, rolls, and 360-degree spins, require significant skill and practice. These maneuvers should only be attempted in a safe, open area, away from obstacles and people, and after mastering the basic flight controls.
- Flips and Rolls: Requires specific button combinations or joystick inputs depending on the drone model.
- 360-Degree Spins: Requires precise control of the yaw axis.
- Precision Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in challenging wind conditions.
Drone Photography and Videography

Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding your drone’s camera features and mastering essential photography techniques. Proper camera settings and stable footage are key to producing compelling results.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
Achieving high-quality aerial photos and videos involves careful planning, precise execution, and a good understanding of camera settings. Consider factors such as lighting, composition, and the drone’s flight path to create visually stunning content.
- Plan your shot: Consider the lighting, composition, and background.
- Adjust camera settings: Optimize aperture, shutter speed, and ISO for different lighting conditions.
- Maintain stable footage: Use features like gimbal stabilization and smooth flight maneuvers.
- Review your footage: Check for quality and make adjustments as needed.
Camera Settings Optimization
Adjusting camera settings like aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is crucial for optimizing image quality in various lighting conditions. Understanding the interplay between these settings is key to capturing sharp, well-exposed images and videos.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the lens.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the length of time the sensor is exposed to light.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity of the sensor to light.
Achieving Stable Footage, How to operate a drone
Minimizing camera shake is essential for producing professional-looking aerial footage. Utilizing the drone’s gimbal stabilization and employing smooth flight techniques significantly improves video quality.
- Use the drone’s gimbal stabilization features.
- Avoid sudden movements and jerky maneuvers.
- Fly in calm wind conditions whenever possible.
- Practice smooth and controlled flight movements.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and preventing unexpected malfunctions. A proactive approach to maintenance minimizes downtime and ensures your drone remains in optimal operating condition.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule should include cleaning the drone, inspecting the propellers and other components, and checking the battery’s health. Software updates should also be applied regularly to benefit from bug fixes and new features.
- Weekly: Clean the drone body and propellers.
- Monthly: Inspect all components for damage or wear and tear.
- Quarterly: Check the battery health and calibrate the drone’s sensors.
- Regularly: Apply software updates as they become available.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Understanding common drone malfunctions and their causes is essential for effective troubleshooting. Knowing how to address these issues quickly and efficiently can minimize downtime and prevent further damage.
- Low Battery Warnings: Land the drone immediately and charge the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Relocate to an area with better GPS reception.
- Propeller Malfunctions: Inspect and replace damaged propellers.
- Motor Issues: Check motor connections and consult the manufacturer’s instructions.
Drone Repairs and Professional Assistance
Basic drone repairs, such as replacing propellers or cleaning sensors, can often be performed at home. However, more complex repairs should be handled by qualified technicians to avoid further damage.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone legally requires understanding and adhering to local regulations and airspace restrictions. Ignoring these rules can lead to fines, legal action, and potential safety hazards.
Legal Requirements and Regulations
Drone regulations vary widely depending on location. Before flying, it’s crucial to research and understand the specific laws and regulations in your area. This includes registering your drone and obtaining any necessary permits or licenses.
Permits and Licenses
In many regions, registering your drone with the relevant aviation authority is mandatory. Specific permits or licenses might be required for commercial drone operations or flights in restricted airspace. Always check the specific regulations in your area.
Airspace Restrictions and Prohibited Areas
Airspace restrictions exist around airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas. Flying in these restricted zones is illegal and can be dangerous. Using online tools and apps to identify restricted airspace is highly recommended.
Responsible Drone Operation
Responsible drone operation emphasizes safety, respect for privacy, and adherence to all applicable laws and regulations. Flying responsibly contributes to a safe and enjoyable drone environment for everyone.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is vital for safe drone operation. Having a plan in place for unexpected events can minimize risks and ensure a successful outcome.
Drone Malfunction or Emergency Procedures
In case of a drone malfunction, the first step is to assess the situation and attempt to regain control. If control cannot be regained, prioritize a safe landing procedure, minimizing the risk of damage or injury.
Safe Drone Recovery After a Crash
If your drone crashes, carefully inspect the damage and assess the safety of the situation before attempting recovery. Be mindful of potential hazards in the crash site and prioritize safety.
Loss of Control or GPS Signal Failure
Loss of control or GPS signal failure can be serious situations. If possible, engage the Return-to-Home (RTH) function, if available. If RTH fails, attempt to manually guide the drone to a safe landing area.
Emergency Contact Information and Resources
Keep a list of emergency contact information readily available, including local emergency services and drone support providers. Having access to these resources can be crucial in emergency situations.
Successfully operating a drone requires a blend of technical skill, safety awareness, and legal understanding. This guide has provided a foundational framework for responsible drone piloting, covering pre-flight procedures, flight controls, various maneuvers, photography techniques, maintenance, legal compliance, and emergency protocols. By consistently applying these principles, you can confidently and safely explore the exciting possibilities of aerial flight while respecting the regulations and ensuring the safety of yourself and others.
Remember, continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone operator.
Common Queries
What is the maximum flight time for most consumer drones?
Flight times vary greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge for many consumer-grade drones.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific rules and regulations in your area. In many places, registration is required for drones above a certain weight.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Immediately engage the “return-to-home” function if available. If that fails, attempt to visually locate the drone and try to regain control. If unsuccessful, report the incident to the relevant authorities.
What is the best way to clean my drone?
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and knowledge of its controls, and a great resource to learn this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This guide covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, ensuring you can safely and effectively operate your drone.
Mastering the skills outlined will greatly enhance your drone flying experience.
Use a soft, dry cloth to gently wipe down the drone’s body. Avoid using harsh chemicals or water. For more stubborn dirt, use a slightly damp cloth.